As the ubiquity of smartphones and tablets increases, offering seamless connectivity has become an integral and competitive aspect of an instant operator’s services. The mobile industry landscape is evolving, spurred on by the introduction of 5G and innovative new spectrum options. Recognizing this, Ecosmob and its expertise established a sophisticated working group to craft an enhanced architectural blueprint for the MVNO network. This dynamic group aims to investigate new converged architectures that leverage our members’ wireless implementations. Simultaneously, they emphasize the impact and benefits of MVNO solutions for existing deployments. It also underscores the features that MVNO solutions and networks must support.
Understanding MVNO Workflow and Standards
According to Report, “the worldwide Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO) market was valued at approximately USD 78.15 billion in 2022. It is projected to reach around USD 149.13 billion by 2030.”
The Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs) are a business, not a network, and never be driven by the network. The central point of wholesale is the resale of excess capacity. Existing fixed or other operators are the ones who fall into this trap the fastest. MVNOs have carved out a niche by providing custom, flexible, and often less expensive services than traditional operators in the bustling telecommunications industry. It has become possible through unique MVNO network architectures and workflows driven by the rise of MVNO solution development. In this article, we dive deep into these concepts and how they form the core of every successful MVNO.
The MVNO Network and Architecture
Understanding the MVNO architecture requires us to dissect the various components involved. The essential part of an MVNO network is the core network, which is either leased from an MNO or built and managed independently, including crucial elements such as the Home Location Register (HLR), Visitor Location Register (VLR), Authentication Center (AuC), Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN), and Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN).
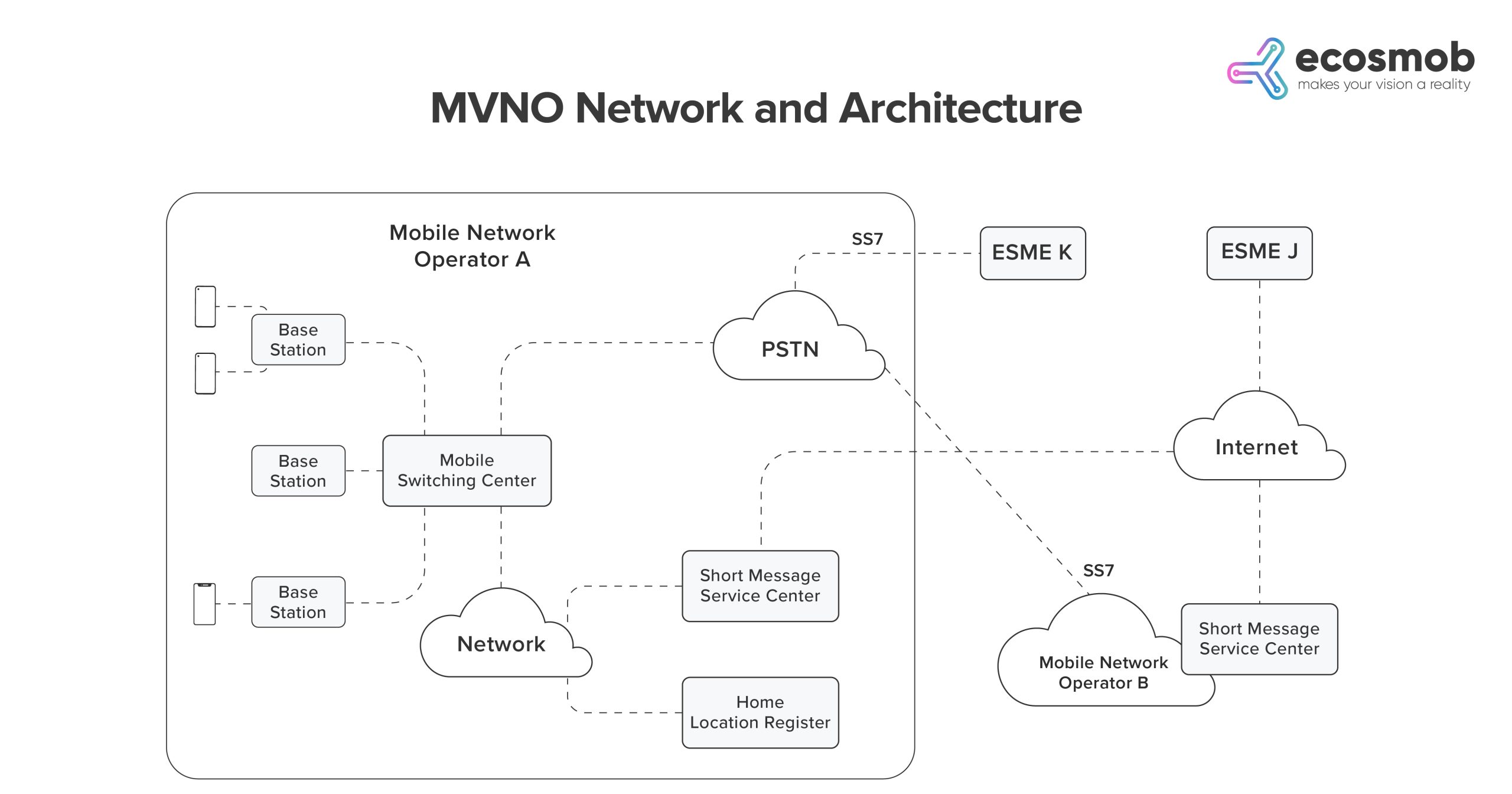
The critical distinction between an MNO and an MVNO is based on their respective approaches to managing the core network.
The MVNO model may be split into three types based on this:
- Skinny MVNO
- Thick MVNO
- Full MVNO
In the Skinny MVNO model, the MVNO has minimal control over the infrastructure, primarily managing sales and marketing. A Thick MVNO controls the HLR, enabling it to independently handle aspects like billing and customer relations management. Lastly, a Full MVNO maintains the core network infrastructure, barring radio stations access network.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of MVNO Workflow
MVNOs rent bandwidth from MNOs, which contain the physical network infrastructure. A string of processes defines the MVNO workflow, all directed at facilitating seamless connectivity for the finished user. The MVNO workflow simplifies it into the following steps:
Market Research and Business Planning
- Identify the market and demographics for the MVNO services.
- Conduct a competitive analysis to know existing MVNOs and MNOs in the region.
- Develop a small business plan outlining your MVNOs objectives, pricing strategy, and revenue model.
Network Selection and Agreement
- Approach various MNOs to discuss potential partnerships and network access agreements.
- Negotiate terms and conditions, including pricing, quality of service, and the scope of services.
- Sign a network access agreement with the chosen MNO to use their infrastructure and services.
Administrative Adherence
- Obtain necessary licenses and access to operate as an MVNO in the target region.
- Ensure compliance with local telecommunications regulations and guidelines.
Service and Product Development
- Develop and customize mobile service plans, packages, and pricing based on your target market’s needs and preferences.
- Create additional value-added services like data bundles, international roaming plans, or content offerings.
Branding and Marketing
- Develop an advertising strategy and brand identity to advertise your MVNOs services.
- Create marketing materials, advertisements, and promotional campaigns.
- Policy for customer acquisition and retention initiatives.
IT Infrastructure and Billing System
- Put up the IT infrastructure to guide customer management, billing, and service provisioning.
- Implement a billing system that may handle various service plans and billing cycles.
SIM Card and Distribution Setup
- Obtain SIM cards branded along with your MVNO logo and information.
- Establish distribution channels to create SIM cards and starter kits offered to customers, such as stores, online sales, or partnerships with other businesses.
Customer Support and Care
- Create support channels for inquiries, complaints, and technical assistance.
- Train support agents to deal with customer issues promptly and effectively.
Launch and Operations
- Launch your MVNO services with an advertising campaign to attract customers.
- Monitor network performance and customer usage to ensure quality service.
- Regularly analyze customer comments and usage patterns to boost services and address their issues.
Continuous Improvement and Expansion
- Continuously review and optimize your service offerings centered on market feedback and competition.
- Consider expanding your MVNO services to other regions or introducing new services as your company grows.
Maintaining a solid relationship with the underlying MNO is essential throughout the workflow because they provide network access and ensure an easy user experience for MVNO customers.
MVNO Standards
Currently, “the MVNO market is valued at approximately USD 61.9 billion, with projections suggesting a surge to USD 91.63 billion by 2026,” according to a Mordor Intelligence report. Anticipated growth factors include the rise of e-SIM, 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), AI, ML, and edge computing, all presenting promising business opportunities for MVNOs shortly.
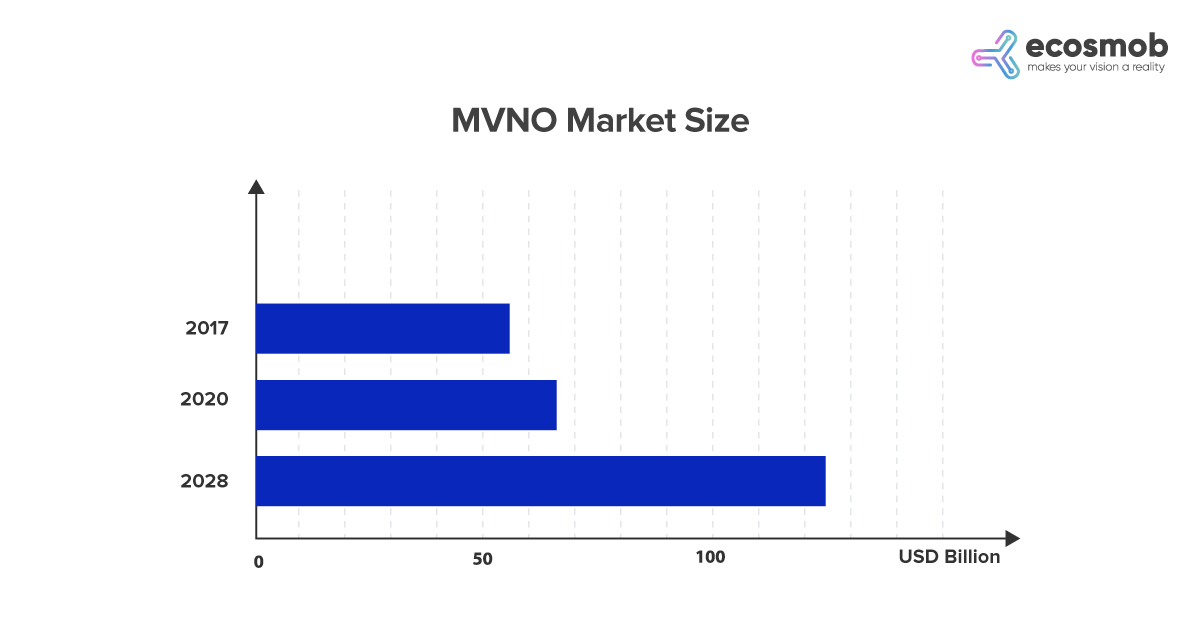 Source: Analytics predict that the MVNO market size will continue to grow
Source: Analytics predict that the MVNO market size will continue to grow
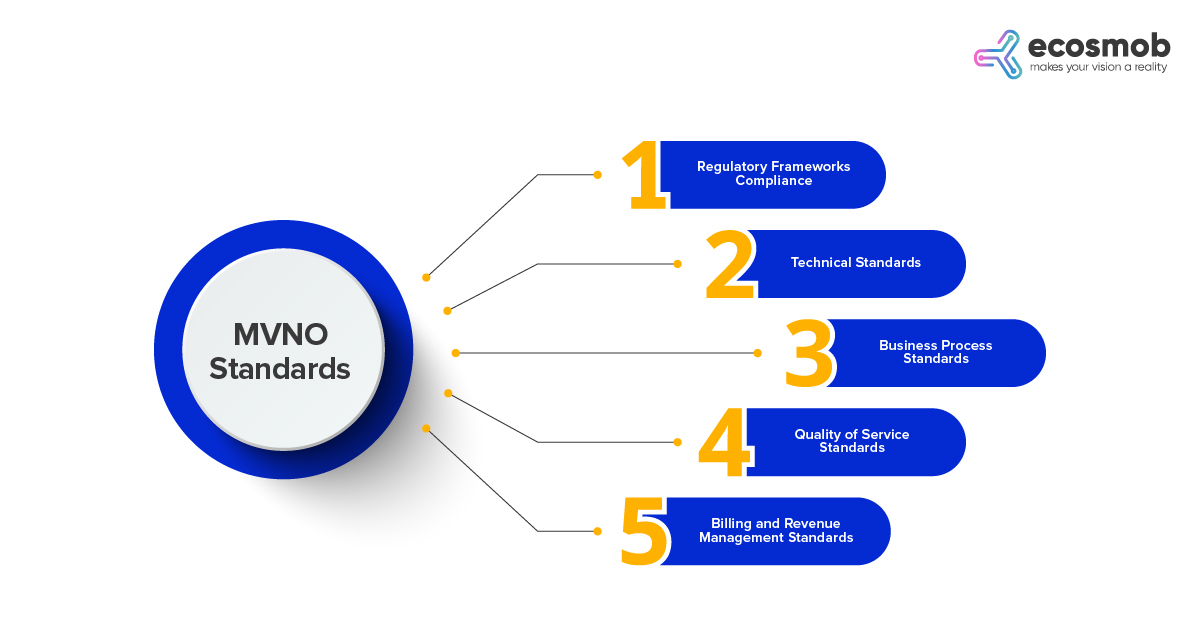
MVNOs adhere to several industry standards to guarantee the smooth functioning of MVNO operations and maintain the integrity of the telecommunications industry. Let’s delve right into a few key ones:
Regulatory Frameworks Compliance
MVNOs operate within the telecommunications regulatory frameworks set by governing bodies. It offers compliance with standards linked to customer data privacy, fair competition, quality of service, and more. These regulatory frameworks vary by jurisdiction, which makes it necessary for MVNOs to know and stick to the regulations within their operational regions.
Technical Standards
Technical standards guide how MVNOs engage with the MNO’s infrastructure, ensuring that MVNO services work smoothly across different networks. It offers measures like 3GPP for mobile telecommunications, IEEE for networking, and ITU for international telecommunications. Staying with these standards helps guarantee interoperability and compatibility between networks and services.
Business Process Standards
Along with technical standards, MVNOs must conform to business process standards. For instance, the TM Forum’s Business Process Framework (eTOM) has an extensive, industry-agreed, and multi-layered view of the critical business processes required to execute an effective, efficient, and agile digital enterprise.
Quality of Service Standards
Ensures that MVNOs maintain an advanced degree of service quality. These standards may dictate minimum service uptimes, maximum call drop rates, and other performance metrics. MVNOs should implement robust monitoring and management systems to track their performance against these standards continuously.
Billing and Revenue Management Standards
These are critical for MVNO operations. Standards in this region guide how MVNOs should bill their customers and manage their revenues. It provides criteria for billing accuracy, dispute resolution, and revenue sharing with MNOs.
Future of MVNOs Opportunities and Challenges
MVNOs have the potential to significantly disrupt the telecommunications industry by bringing innovative, customer-centric services to the market. However, achieving this potential requires deeply comprehending the MVNO workflow and adherence to industry standards. Moreover, MVNOs face several challenges, including negotiating favorable network access agreements with MNOs, differentiating their services in a competitive market, and maintaining high customer satisfaction.
To navigate these challenges, MVNOs certainly need to leverage the newest technologies. For instance, artificial intelligence can personalize customer offerings and improve customer support, while blockchain supplies a protected and transparent billing and revenue management platform. By adopting such technologies and focusing relentlessly on customer needs, MVNOs can position themselves for success in the evolving telecommunications landscape.
Role of MVNO Solutions
Leveraging the market Value of MVNO solutions to streamline their operations. These range from Billing and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems to Value-Added Services (VAS). The biggest thing would be to find the appropriate MVNO solution provider.
Billing systems ensure that each call, message, or byte of data the buyer consumes is accurately tracked and billed. On the other hand, CRM systems allow MVNOs to deal with customer interactions, providing a platform for sales, customer support, and marketing.
VAS services aren’t a section of the core offering (voice calls and data) but add value to someone’s experience. Examples include voicemail, call forwarding, mobile banking, and more. VAS gives MVNOs a competitive edge by differentiating their services from other providers.
Read More: How MVNOs Benefit Telecom and Retail Domains?
Guidelines for a couple of major critical roles of MVNO solutions
Here are some of the adequate instructions given below:
- Enhancing Competition: Frequently target underserved niche markets by established network carriers. For instance, they provide affordable plans for low-income customers, specific trip packages, or niche services for corporate clients.
- Filling Market Gaps: Focus more on developing novel services and distinctive MVNO solutions because they don’t have to worry about network infrastructure. For instance, some MVNOs provide services packaged with other goods or concentrate on providing digital-first experiences.
- Innovative Services: As MVNOs don’t have to focus on network infrastructure, they can devote more resources to creating innovative services and unique offerings. For instance, some MVNOs offer bundled services with other products or focus on digital-first experiences.
- Efficient usage of Network Infrastructure: Rent network capacity from Mobile Network Operators (MNOs), which can help effectively utilize the already-existing network infrastructure. It can be helpful in markets with a lot of unused network bandwidth.
Additionally, MVNOs can connect to the MNOs’ network infrastructure and occasionally supply data and insights to help the MVNO enhance its services.
Choose MVNO Solution Provider with Ecosmob Technologies
An efficient MVNO solution provider knows the early requirements and difficulties MVNOs face. Ecosmob provides scalable and adaptable solutions that help MVNOs fulfill the expectations of a market often undergoing fast change. In addition to other services, we also offer network configuration, operational assistance, VAS integration, billing, and CRM solutions. In a word, the MVNO model provides a unique method of service delivery. It relies on effective workflows, sturdy architecture, and several MVNO solutions to provide value to the consumer. Selecting the finest MVNO solution provider is crucial for MVNOs to succeed in this cutthroat environment. MVNOs can create a customer-centric strategy differentiating them from traditional operators by utilizing cutting-edge technologies and adjusting to shifting market circumstances.
Wondering About Streamlining Your MVNO Journey With Us?
FAQs
How does an MVNO operate?
MVNOs lease wireless capacity from MNOs, and provide mobile services to their customers using this leased capacity. MVNOs manage customer relationships, billing, customer care, and other front-end functions while relying on the MNO for network services.
What are the different types of MVNOs?
Several types are based on the depth of service and operational responsibility:
- Branded Reseller: Least involved; they only handle marketing and branding.
- Service Operator: Manages customer service and billing but depends significantly on the MNO for network services.
- Enhanced Service Operator: Offers additional services, such as unique billing plans or bespoke mobile applications.
- Full MVNO: Runs almost everything except the radio network, including their core network infrastructure.
What Standards Govern MVNO Operations?
MVNO operations are primarily governed by the terms of their commercial agreements with MNOs. However, they must also comply with local and international telecom regulations and standards, which vary by country. For example, in many countries, MVNOs must meet certain quality of service (QoS) standards, customer data privacy regulations, and emergency call handling requirements.
How do MVNOs differentiate themselves from MNOs or other MVNOs?
MVNOs often target specific market niches that are underserved by traditional MNOs. They may focus on particular demographics, offer unique pricing structures, cater to travelers with international roaming packages, or provide bespoke content and services tailored to a specific group. Innovation in customer service, billing, and bundled services is a key differentiator.
Do MVNOs impact network quality or service?
Ideally, no. MVNOs purchase a predefined amount of network capacity from MNOs. The MNOs are responsible for ensuring that their networks handle the combined load of their direct customers and the MVNO’s subscribers. However, during heavy network congestion, MVNO customers might experience a lower priority in data speeds or connectivity compared to direct MNO subscribers, depending on the agreement between the MVNO and MNO.















