The telecom industry isn’t just about making calls and sending text messages anymore; it’s a complex ecosystem that powers the digital world. With many acronyms and complex relationships, understanding the ecosystem becomes critical for tech-savvy consumers, telecom professionals, and software developers. This comprehensive guide dives deep into four pivotal entities: MNO, MVNO, MVNE, and MVNA, detailing their roles, underlying technologies, types, and future trends.
Mobile Network Operator (MNO)
MNOs are the giants in the telecommunications world. They own the physical infrastructure necessary for mobile services, including cell towers, servers, spectrum licenses, and networking equipment. They build and sustain the mobile networks essential for phone calls, text messaging, and web browsing.
Infrastructure of MNOs
- Radio Access Network (RAN): Comprises the cellular base stations (BTS) connected to antennas that facilitate mobile communication.
- Core Network: Involves multiple components such as MSC (Mobile Switching Center), HLR (Home Location Register), and VLR (Visitor Location Register) for call routing and subscriber data management.
- Transmission Network: Fiber-optic cables connecting different RAN and Core Network parts.
- OSS/BSS Systems: Operation Support Systems and Business Support Systems that manage billing, CRM, and network optimization services.
Responsibilities & Capabilities of MNOs
- Network Infrastructure: Building and maintaining cell towers, fiber optic cables, and data centers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to government regulations for spectrum use and customer data.
- Billing and Customer Service: Offering direct customer relations, from sales to technical support.
Technical Challenges
- Spectrum Management
- MNOs face the challenge of efficiently using licensed spectrum bands while also adhering to government and international regulations.
- To address this, they use advanced tools and algorithms for dynamic spectrum allocation to adhere to regulatory norms.
- Network Load Balancing
- Managing high traffic volumes, particularly during peak hours, is another major challenge.
- To manage high traffic, MNOs deploy load-balancing techniques that distribute data across multiple servers, reducing delays.
- Latency and QoS
- Ensuring low latency and high Quality of Service is especially crucial for applications like VoIP and streaming services.
- For this low latency and high QoS, MNOs invest in edge computing and optimized routing algorithms.
Future Trends
- 5G Adoption: Enhancements in speed and lower latency.
- AI Integration: Predictive analytics and intelligent automation.
Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO)
MVNOs are the boutique shops of the mobile world. The global MVNO market is expected to grow from USD 66.13 billion in 2023 to USD 91.68 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 6.75%.
Interestingly, MVNOs don’t own the hardware; they lease or buy bandwidth from MNOs to offer specialized or localized services to niche markets. MVNOs often utilize custom MVNO solutions development to tailor their services more precisely.
How They Operate
An MVNO forms a business agreement with an MNO to acquire bulk access to network services at wholesale rates. Then, it sets its retail prices independently.
Infrastructure of MVNOs
- Service Delivery Platform (SDP): Tailors services like content delivery, often using specialized MVNO Solutions.
- HSS/HLR: Manages customer profiles and services.
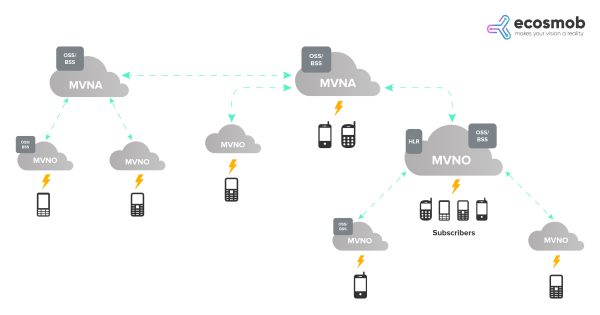
Types of MVNOs
- Thick MVNO: Owns network elements like the HLR, allowing more control over services and subscriber data.
- Thin MVNO: Leases almost all network elements from the MNO, thus having lesser control and a quicker go-to-market strategy.
- Branded Reseller: Has no operational control and relies solely on the MNO’s existing services and infrastructure.
Future Trends
- Niche Marketing: Specialization in IoT, elderly care, etc.
- Blockchain: For secure and transparent billing, sometimes facilitated through custom MVNO solutions development.
Mobile Virtual Network Enabler (MVNE)
MVNEs offer the technical solutions that enable MVNOs to function. They are essentially B2B services that provide the technology stack required for MVNO operations but don’t offer mobile services to end consumers.
Infrastructure of MVNEs
- MVNE Platform: Custom MVNO solutions and pre-configured MVNO billing solutions for billing and customer care.
- API Gateway: Enables easy third-party integrations.
Responsibilities & Capabilities of MVNEs
- Platform Services: Provide software solutions for billing, operations, and customer relationship management (CRM).
- Regulatory Support: Ensure compliance with telecom regulations.
- Network Connectivity: Facilitate the connection between MVNOs and MNOs.
Who Needs an MVNE?
Smaller MVNOs that lack the infrastructure and technical capabilities can accelerate their market launch through MVNE’s MVNO solutions.
Future Trends
- Cloud Integration: Agility in scaling services.
- API Economy: More open APIs for robust third-party integrations.
Mobile Virtual Network Aggregator (MVNA)
MVNAs act as a bridge between MNOs and multiple MVNOs. They negotiate contracts with MNOs for bulk services and redistribute these to MVNOs, often providing a one-stop operational platform.
Infrastructure of MVNAs
- Aggregation Platform: Manages resources and billing for multiple MVNO clients.
- CDR Management: For accurate billing across MVNOs.
Responsibilities & Capabilities of MVNAs
- Multi-Tenant Platform: Allows MVNOs to share resources like billing systems, thereby reducing costs.
- Gateway Services: Provide APIs for MVNOs to access services like SMS, MMS, and data.
- Network Slicing: Allows partitioning of network resources among multiple MVNOs.
Future Trends
- Smart Contracts: For automated, transparent dealings.
- IoT and Edge Computing: Facilitating more robust and localized services.
Wondering About Streamlining Your MVNO Journey With Us?
Comparative Summary
| Criteria | MNO | MVNO | MVNE | MVNA |
| Infrastructure | Physical & Software | Mostly Software | Platform & APIs | Aggregation Platform |
| Service Control | Full | Partial | Backend | Limited |
| Services Provided | Full telecom services | Specialized telecom services | Operational support | Bulk network access & shared services |
| Advanced Tech | SDN, NFV, AI | Data Analytics, IoT | Cloud, API Gateway | Smart Contracts, Edge Computing |
Conclusion
Each of these entities—MNO, MVNO, MVNE, and MVNA—plays a distinct and crucial role in the vast mobile telecommunications ecosystem. Understanding their functions, responsibilities, and interdependencies is vital for anyone looking to venture into this industry or make informed decisions as a consumer.
By comprehending these nuances, you are gaining a robust understanding of how the mobile telecom universe functions.
Let us help you navigate this landscape with custom MVNO and billing solutions tailored to your needs. Schedule a call with one of Ecosmob’s MVNO experts today!