MVNO is the Mobile Virtual Network Operator.
These are considered “virtual” mobile operators because they do not own their infrastructure. Instead, they lease the mobile network from MNOs. No wonder you have already read this information numerous times. Therefore, Ecosmob presents more exciting and vital facts that you must know about MVNO solutions development.
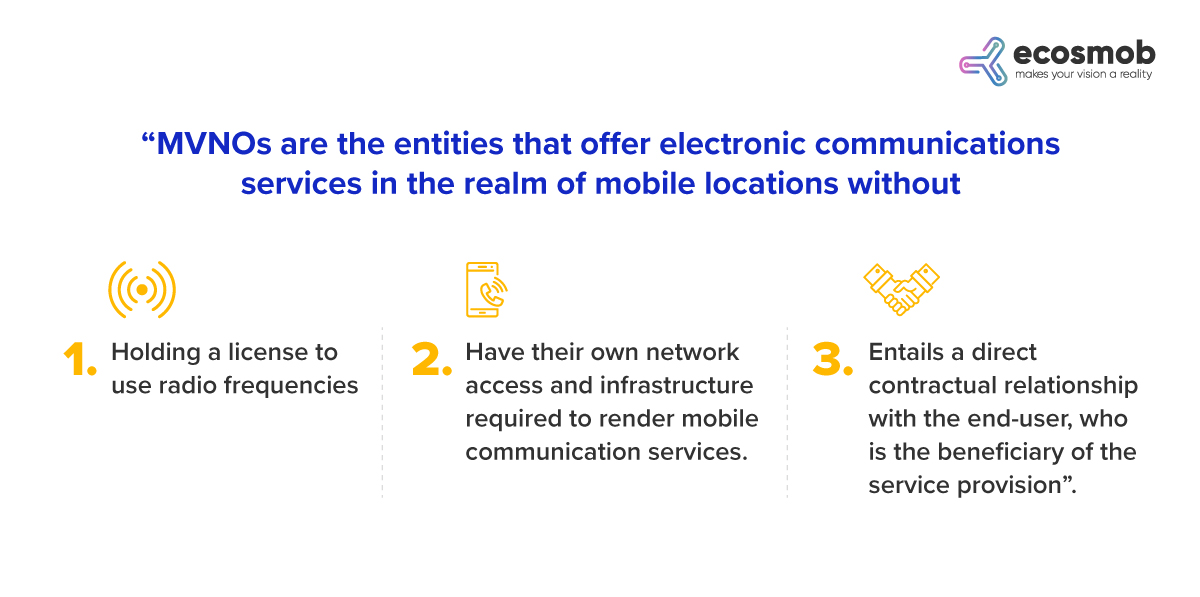
MVNOs, Ideally, are the entities that establish and present their unique retail offerings to the market. These retail offers can vary from those presented by MNOs hosting MVNOs. This distinct retail proposition is a defining component that shapes MVNOs’ unique business strategies.
In today’s digital world, where the Rise of MVNO has become synonymous with virtualization, MVNOs are expanding exponentially by adopting advanced technologies like AI, ML, edge computing, and e-SIM, with 5G and IoT in the driving seat, giving acceleration.
“Analyzing the market dynamics, competitive landscape, recent developments, and future opportunities, a report by Mordor Intelligence predicts Asia-Pacific MVNO Market revenue to Reach USD 50.05 billion by 2028”.
All the research and internationally accepted definitions of MVNOs conclude-
 How does MVNO Work?
How does MVNO Work?
MVNOs act as an intermediary between MNOs and customers. They develop their service plans with distinctive features, pricing, and branding after purchasing bulk network capacity from MNOs at wholesale rates. While utilizing the MNOs’ physical network infrastructure, MVNOs are responsible for subscriber management, marketing, and customer service.
MVNO Business Model
The whole concept of MVNOs revolves around collaboration and partnership. Unlike traditional mobile carriers (Check Top 8 Differences Between MVNOs and Traditional Operators) that invest heavily in building infrastructure and its maintenance costs, MVNOs primarily focus on offering innovative and flexible service plans while leveraging infrastructure benefits from MNOs. This partnership allows MVNOS to save recurring expenditures on building and maintaining a network infrastructure.
MVNO Components and Ecosystem
The ecosystem of MVNO comprises various components that function together to ensure the successful provisioning of mobile services to subscribers. These components include,
1. Network Infrastructure
When we mention the network infrastructure of MVNOs, MNOs should be the first thing to consider. MVNOs rely on MNOs not only for physical infrastructure but also for base stations, network equipment, and antennas.
The MNO’s network infrastructure includes base stations, switching equipment, and data centers.
2. MVNO Core Network
Includes elements such as
- Home Location Register (HLR) – A database that stores subscriber’s information, location, and mobility data for call routing and service provisioning.
- Authentication Center (AuC)- Ensures secure communication by subscriber authentication and encryption key generation.
- Gateway Mobile Switching Center (GMSC)-Connects the calls between different mobile networks, ensuring smooth communication between subscribers of other networks.
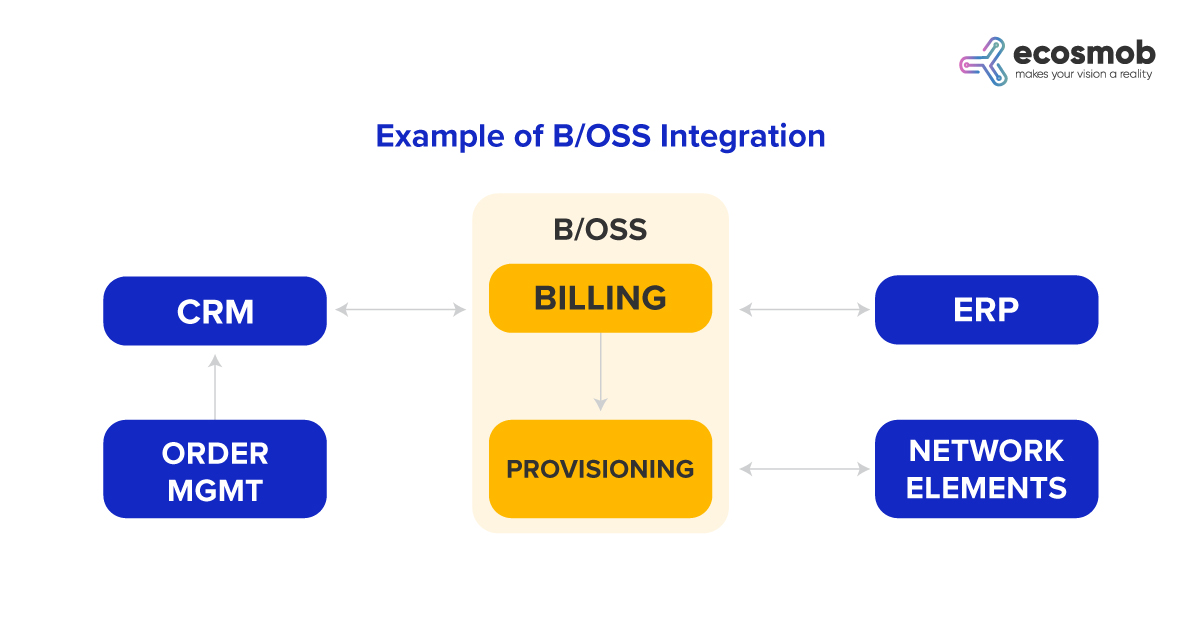
3. BSS System
- CRM- Customer Relationship Management component of MVNO handles subscriber data, conversations, and customer preferences that enhance customer experience.
- Provisioning and Activation- Ensure smooth onboarding of new subscribers by automating service provisioning.
- Billing and Rating- Applies pricing policies, generates bills, and tracks subscriber usage and their by-rates services on consumption.
 4. OSS Systems
4. OSS Systems
The network operations center monitors and handles network operations, performance, and troubleshooting.
Configuration management network configuration changes while ensuring the smooth functioning of the system.
For MVNOs to gain a competitive advantage over MNOs and other MVNOs is possible ‘by leveraging the capabilities of components under MVNO control and delivering robust and timely services in the market”. This is possible with B/OSS, which gives MVNO billing and provisioning functionalities.
Types of MVNO
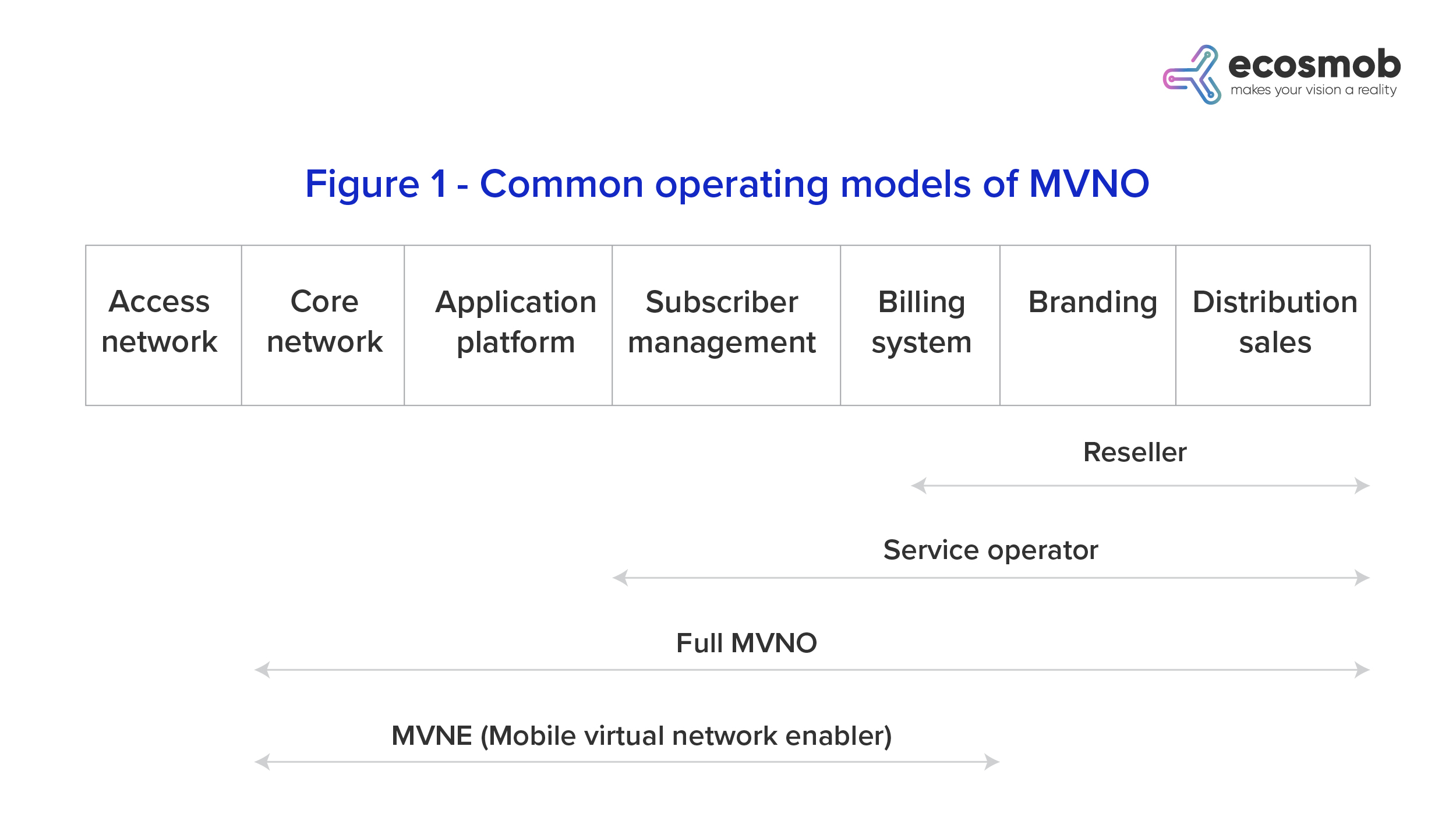 Full MVNO
Full MVNO
Holds greater control over its services in the retail market. A full MVNO operates its core network elements for greater flexibility in design and promotes implementing new services.
These mobile core components are used-
- For service provision
HLR/HSS (user register), VLR, (G)MSC, EIR, AuC, (G)SMSC and, SGSN - For data services
PCRF (policy management), P-GW (gateway) - For call and messaging services
IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem a next-generation switch)
Full MVNOs can issue their SIM cards. However, as discussed earlier, they do not hold usage rights over radio frequencies. For this reason, a full MVNO also does not have elements of the radio access network (e.g., base stations radio network controllers).
MVNO is a new-age telecom synonym. Adopt it today.
1) Light MVNO
MVNOs of this category are the “distributors.” Light MVNOs can issue their own SIM cards under their brand name. It is also important to note that Light MVNOs do not hold a network infrastructure but offer a means that ensures the control of the relationship with the user.
In contrast to full MVNOs, Light MVNOs rely more on MNOs for billing, network management, and customer support.
2) Medium MVNO
Based on the types of services offered and the degree of independence from MNOs, various kinds of Mobile Virtual Network Operators range between light and Full MVNO types. These can be divided into two subcategories:
- Service provider MVNOs
This type of MVNO takes care of all customer relations and billing services processes.
- Value-Added Service (VAS) provider MVNO’s
This type of MVNO possesses specific infrastructure components that grant complete control over the services provided. These MVNOs offer VAS services like voice messaging, notifications for missed calls, virtual private networks (VPN), and more.
3) MVNE
Another MVNO type is MVNE, which is comparatively recent in the mobile communications market. MVNE is the service integrator that aims to grant the “would-be” MVNOs core network and infrastructure solutions for different services. These services can range from providing core network elements to ensuring administrative and operational support.
MVNEs can also be seen as an intermediary between the MVNOs and the host MNOs.
Overall, the mentioned generic type of MVNOs illustrates the vast diversity of an operational model that encompasses the concept of MVNO. What is more interesting to note here is that MNOs and the entities interested in becoming MVNOs have free will to choose the operational model that suits their particular interests and business strategy. For more clarity and expert advice, you can always contact us.
Launching your MVNO
One of the simplest ways to launch your own MVNO is to go with a “thin MVNO.” These MVNOs have most of the infrastructure supplied by an MNO itself. Additionally, there is no requirement for capital investment in a mobile core (an EPC) or radio network since these come as a rented service from MNOs.
MNOs also facilitate MVNOs to implement their own B/OSS (Business and Operation Support System), which is crucial for billing, service provisioning, and customer management. B/OSS must also be integrated with varied EPC components.
Let us see how it works,
A SIM card is activated in HLR/HSS and provisioned in various components like PCRF when a customer name is entered.
Once a customer uses the service, the MVNO receives CDRs in the billing system, which is later processed.
MNOs and MVNOs share a fruitful partnership. MNOs render technical capacity deployment, customer acquisition, and retention; on the other hand, MVNOs add value to the radio network and coverage offered by MNOs.
Benefits of MVNO
 In its generic form, telecommunication connects individuals, communities, and businesses. And the list of MVNO benefits continues. It has a lot to offer to enterprises and the consumer base.
In its generic form, telecommunication connects individuals, communities, and businesses. And the list of MVNO benefits continues. It has a lot to offer to enterprises and the consumer base.
MNOs offer comprehensive services with a standardized approach to reach millions of consumers and businesses. Whereas MVNOs provide services to specific market segments with more personalized services suitable for the customer’s needs. Since MVNOs are not required to focus on a larger workforce, infrastructure, network investments, and maintenance, they own higher customer satisfaction ratings.
As mentioned, Mobile Virtual Network Operators utilize network capacity without owning it. MVNOs can pass down this cost-benefit and offer their customers competitively without compromising quality.
With globalization, different enterprises require various plans for their customer base and targeted market. For instance, some businesses may demand long-distance call plans with high-speed data. In comparison, some social networking businesses may need more Gigas to browse social networks. MVNOs cater to all the diverse requirements of their users with flexible options due to their network infrastructure independence.
Broad device compatibility and no credit checks for potential customers and telecom operators are also the most celebrated benefits of MVNOs. Furthermore, referring to the Benefits and Market Value of MVNO For Telecom Operators gives you more detailed insights.
What’s New in MVNO Offerings
1. More Features
With ever-increasing technological advancements and competition, call control, conferencing, call recording, web access & services, device groups, customized apps, and number management have become essential parts of a sophisticated MVNO offering.
2. Offloading
Software and handset configuration that requires the MVNOs to offer customized services to sellers and consumers. Offloading options minimize the total cost by using alternative methods for the same type of service that a user gets from a regular cell tower. These services include free entry-level plans, free VoIP, and messaging over WiFi with cellular as an add-on.
MVNO Market Overview
The MVNO market has become a highly competitive place due to the presence of several players. Improved regulatory environments, widespread adoption of e-SIM, and implementation of 5G technology are some of its driving forces. The impact of 5G on MVNO and the Wireless Wholesale Market alone is one of the hot talks of the telecom market.
The ever-increasing demand for affordable voice and data services is paving the way for MVNOs to offer bundled services at lower prices than MNOs. In the Asia-Pacific region alone, there will be 1.8 billion unique mobile customers by 2025, per GSMA predictions, where India will be a significant contributor.
Different geographies act differently to a technology. The geographical development, customer base, and market demand all affect the slope of MVNO. Saudi Arabia, for instance, being one of the largest ICT markets in the Middle East region, owns a highly competitive telecom sector.
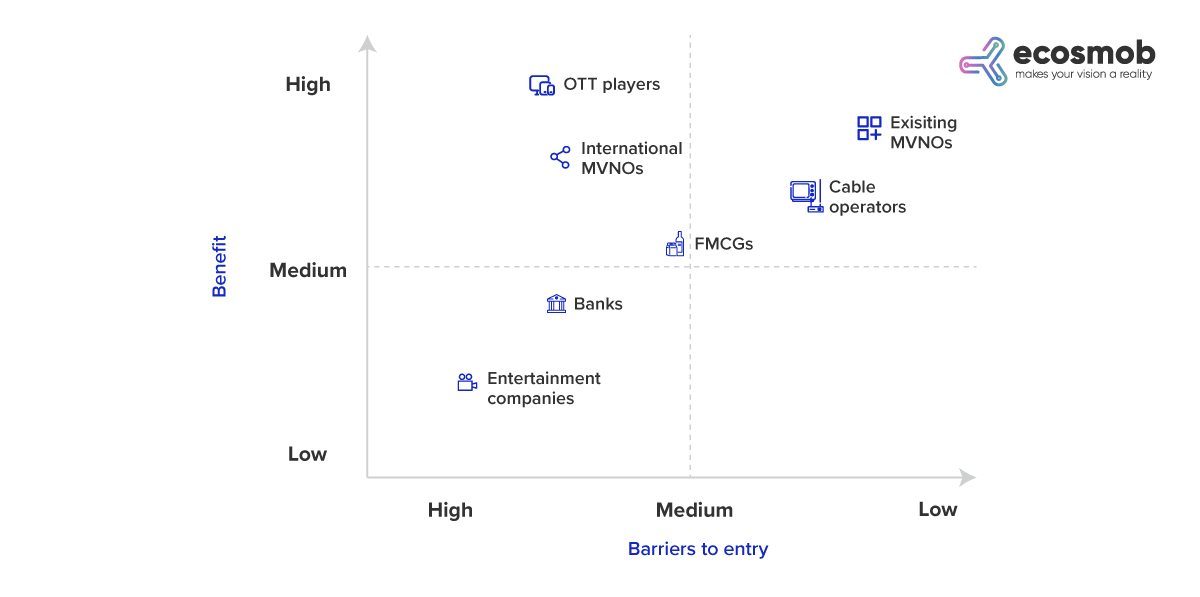
Other Market Players with an Opportunity to Become an MVNO
Domestic and international DTH operators, OTT players, FMCG, retail enterprises, and significant content and media players hold a more substantial opportunity to enter the telecom service stream. These players who have already been outlining the connectivity business have the customer base and market expertise. Let us look at the image given below for more clarity:
 Wrapping Up
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, understanding MVNO, its components, and various market aspects is crucial before making any business decision. With Digitization and ever-increasing market competition, the MVNO market has come a long way. Today, MVNO focuses on micro-segments and subscriber value. Thereby, from network architecture to subscriber management specialized services and continuous innovations, MVNO offers over-the-top services. Contact us today for more insights on MVNO and customized MVNO solutions while experiencing excellent communication at your fingertips.
The world is connecting better with MVNOs. Why aren’t you?
FAQs
Q. How do you choose the right MVNO?
A. Choosing MVNO involves considering factors like- accessing network coverage, plan pricing, customer reviews, data speed, and additional features. Therefore, it is essential to carefully access the requirements and compare the MVNOs to make an informed decision.
Q. Do MVNOs offer unlimited data plans?
A. Yes, many MVNOs offer unlimited data plans with specific terms and conditions.
Q. Can I switch to MVNOs anytime?
A. Yes, you can easily switch to MVNOs whenever you want. MVNOs mainly offer prepaid plans without any contracts, which gives you all the flexibility to change for better deals and services.
Q. Can I use my phone number while switching to an MVNO?
A. You can keep your phone number through porting while switching to an MVNO.
Q. Can I rely on MVNOs for network coverage?
A. Definitely, yes. MVNOs offer reliable network coverage to customers that yield greater customer satisfaction. However, checking the offered network coverage with your prospect MVNO is always advisable.