As technology advances, it becomes more and more crucial for business leaders to stay ahead of the curve and keep abreast of developments in the telecom sector. Two terms that have become increasingly relevant in recent years are MVNOs and Traditional mobile network operators. We at Ecosmob Technologies have curated a comprehensive guide for you explaining the MVNO concept, the difference Between MVNOs and Traditional Operators, critical players in the MVNO market, and more.
Before we delve into the differences, let’s define what MVNOs and Traditional operators are and highlight the essential aspects of MVNO solutions development and the unique selling points of these providers.
What are Traditional Mobile Operators?
Traditional Operators, or MNOs, are the conventional telecommunications providers in the telecommunication landscape. They own and operate all parts of the necessary infrastructure including the wireless spectrum, network equipment, backend systems, and other resources. Examples include AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile, and many others across the globe.
What is MVNO?
An MVNO, on the other hand, does not own the entire telecom infrastructure. An essential component of an MVNO’s operation is its MVNO solutions, which encompass the software and processes required to provide its services. It includes MVNO billing systems, customer relationship management software, and other operational tools. Developing these solutions requires careful planning and execution to ensure seamless service to their customers.
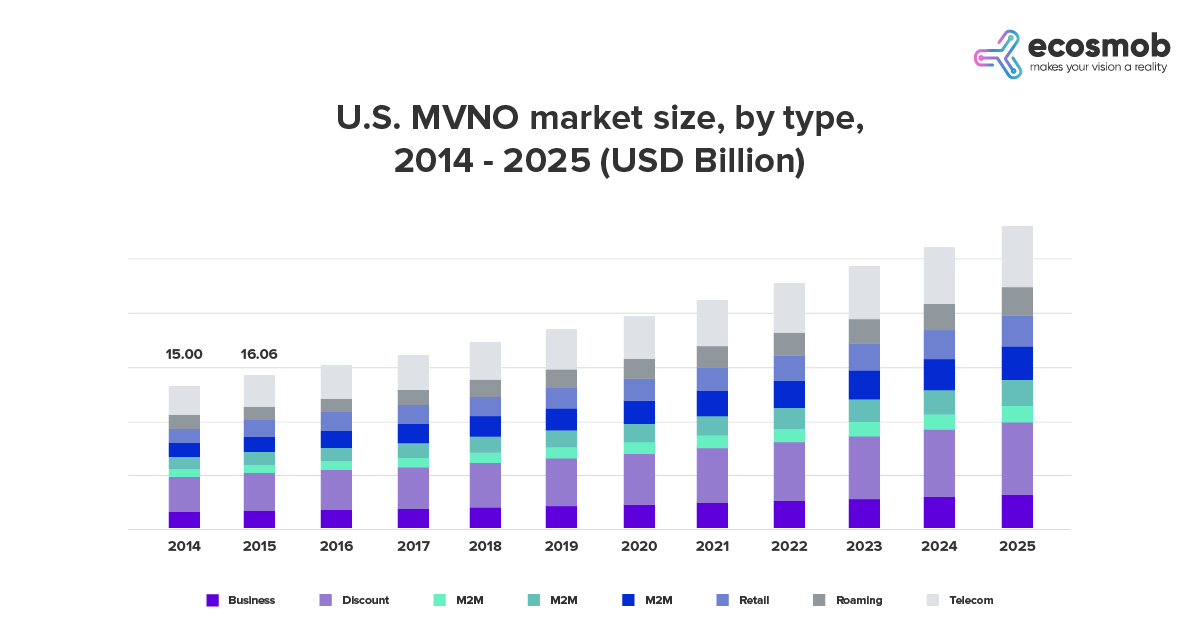
According to Grand View Research, the U.S. MVNO market size was estimated at USD 18.42 billion in 2017 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% over the forecast period. The market is likely to witness significant traction owing to the increasing quantity of mobile subscribers in the region and the rising deployment of 4G and LTE networks.
 Now that we’ve outlined the basics, let’s delve into the significant differences between MVNOs and traditional operators:
Now that we’ve outlined the basics, let’s delve into the significant differences between MVNOs and traditional operators:
Difference Between Traditional and Virtual Mobile Operators
Let’s explore the key differences exhibited between Mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs) and mobile operators with their very own network (Traditional operators), which are given below.
Infrastructure Ownership
As mentioned, Traditional Operators own their network infrastructure, including the wireless spectrum, network equipment, transmission facilities, etc. This ownership allows them total control over their service quality, capacity, and coverage.
In contrast, MVNOs do not own these physical network assets. They rely on MNOs’ infrastructure to deliver services to their customers. However, MVNOs can still offer quality services and control elements like customer service, pricing, and unique value-added features.
Cost and Pricing
Due to the lack of infrastructure costs, MVNO solutions typically have lower operating expenses than MNOs. This difference often allows them to offer consumers more affordable, flexible pricing plans. For instance, MVNOs often target specific market segments with tailored programs, low-cost plans, prepaid options, or data-heavy packages.
Traditional Operators typically have higher operating costs due to infrastructure maintenance but can leverage their network control to offer high-speed data, broader coverage, and more comprehensive service packages.
Market Focus
Traditional Operators usually serve a broader market and have various plans to cater to different consumer segments. They have a global or nationwide presence and offer services ranging from voice, data, roaming, and even ancillary services like streaming and device sales.
MVNOs, in contrast, often focus on specific, underserved market niches. For example, MVNOs target budget-conscious consumers, ethnic communities, or specific age demographics.
Read More: How MVNOs Benefit Telecom and Retail Domains?
Innovation and Agility
Due to their smaller size and less bureaucracy, MVNOs can move quickly to innovate and meet changing customer demands. They have more flexibility in launching new plans, adopting new business models, or leveraging new technologies.
On the other hand, Traditional Operators, while having substantial resources, often need help with agility due to their larger organizational structures. However, they have the advantage of controlling the entire value chain, which can facilitate more holistic innovation, especially at the infrastructure level.
Both Traditional Operators and MVNOs play vital roles in the telecommunications industry, each with unique strengths and approaches. As a business leader, understanding these differences can guide your strategic decisions, whether considering a partnership, looking for a service provider, or planning to enter the telecom market.
The Market Is Switching to Better Communication Solutions. Are You?
Difference Between Traditional and Virtual Mobile Operators
| Traditional Mobile Operators | Virtual Mobile Operators | |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Own physical infrastructure, such as cell towers and equipment, and are responsible for maintenance and upgrades. | Do not own physical infrastructure. Instead, lease network capacity from traditional operators. |
| Cost Structure | High overhead due to the maintenance cost. The upgradation of physical infrastructure often results in higher consumer prices. | Lower overhead due to no infrastructure maintenance cost. This will lead to reducing costs for consumers. |
| Geographic Coverage | Typically offers broad geographic coverage due to their physical infrastructure | Dependent on the coverage capacity of the network they are leasing from, which may be limited in some areas. |
| Service Offering | Usually provide a wide range of services, including voice, data, and other value-added services. | Offers a limited range of services. However, it varies on the agreement with the traditional operator. |
| Flexibility and Innovation | Less flexible due to large size and entrenched systems. | More flexible and able to innovate quickly due to smaller size and lack of physical infrastructure. |
| Customer Support | May have physical stores for customer support. Also, offer phone and online support. | Primarily offer online and over-the-phone customer support as they typically do not have physical stores. |
| Market Entry and Exit | High cost of market entry due to the need for physical infrastructure. Market exit can also be costly and complex. | Lower cost of market entry due to no need for physical infrastructure. Market exit is more straightforward and less expensive. |
| Control over Network Quality | Complete control over network quality and performance. | It depends on the quality and performance of the leased network |
| Business Model | Capital-intensive business model due to infrastructure costs | More service-oriented business model, focusing on customer service and pricing strategies |
Variations In Business Model Aspects
While Traditional Operators and MVNOs provide mobile network services, their business models fundamentally differ. Here are a few key distinctions:
- Service Provider MVNO (Skinny MVNO): MVNOs have the least control over their services. They primarily purchase minutes, texts, and data in bulk from Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and resell them under their brand. They do not have their core network infrastructure and thus rely on MNOs for billing, customer service, network maintenance, and technical issues. Their business model focuses mainly on marketing, sales, and customer relationships. They are considered the least complex MVNO form and the easiest to set up.
- Enhanced MVNO (Thin MVNO/Light MVNO): These MVNOs have more control over their operations than Skinny MVNOs. In addition to marketing and customer relationships, they manage technological aspects like billing and customer service systems. They still rely on the MNO’s network for service delivery, but they may differentiate themselves through unique pricing plans, value-added services, or customer service strategies. They provide a balance between operational control and infrastructural dependence.
- Full MVNO (Thick MVNO): Full MVNO Operators have the most control over their operations. Their core network infrastructure, including the Home Location Register (HLR) and other network components, relies only on MNO’s radio access network. They handle everything from billing, customer service, network operation, SIM card issuing, and more. Their business model allows for the most differentiation and innovation because they control most of their value chain. Full MVNOs require the most resources and technical know-how to set up and operate.
Variations in Business Model Aspect
| Business Model Aspect | Traditional Operators | MVNOs |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Own the entire network infrastructure | Rely on traditional operators’ networks for infrastructure |
| Capital Investment | High, due to infrastructure costs and maintenance | Lower, since they lease network capacity |
| Pricing | Generally higher to recover capital expenditure | Can be more competitive due to lower overhead |
| Service Area | Typically nationwide or international | Dependent on the network, they have agreements with |
| Customer Relationship | Direct, with control over customer service quality | More indirect, reliant on the host network’s service quality |
| Innovations & Services | Less flexible due to the scale of operations | More flexible and quicker to launch new services |
| Market Entry | BarrierHigh, due to regulatory and infrastructure demands | Lower, due to less infrastructure requirement |
So, the significant differences lie in the degree of control an MVNO has over its operations, the services it can offer, and the resources required to operate. With more power, an MVNO can offer more differentiated and potentially innovative services but with greater responsibility and cost.
The Disparity in Commercial Offerings
Competition within this industry is fierce, yielding a plethora of varied proposals. However, Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs) typically offer more economical solutions as they’re free from the cost of upkeeping the entire network infrastructure.
MVNOs display more flexibility and modularity in their services. They make it simpler for consumers to opt only for the required services, enhancing their offerings’ appeal. Plus, they don’t impose lengthy contract obligations.
Due to the lack of extensive network investment requirements, MVNOs can cater to unique market niches. As such, their services and offers are typically tailored to meet the needs of distinct markets, enabling them to access a customer base often overlooked by traditional operators.
However, one notable commercial distinction plays to the advantage of traditional operators. These operators maintain physical stores where customers can address any issues. Plus, their network ownership grants them special access to technical resolutions, leading to more robust customer service provided by these types of operators.
Final Thoughts!
MVNOs and traditional operators differ significantly in network infrastructure ownership, service provisioning, SIM card management, and billing. Understanding the technical distinctions is crucial for organizations looking to develop MVNO solutions or for individuals seeking a deeper understanding of the telecommunications landscape.
With this in-depth comparison guide, you can make an informed decision and choose a telecom provider that suits you the best. Feel free to contact us at Ecosmob Technologies if you require more expert insights. Our representatives are always there to fix your on-time issue.
MVNOs or Traditional Operators? Discover Your Ideal Connection in Just a Click.
How do MVNOs differ from traditional operators?
The main difference lies in the ownership and control of the network infrastructure. Traditional operators invest heavily in building and maintaining their network infrastructure, while MVNOs rely on leasing network capacity from MNOs. This distinction affects coverage, network quality, and control over service offerings.
Does the choice between an MVNO and a traditional operator affect coverage?
Yes, coverage can be affected. Traditional operators typically have extensive network infrastructure, allowing for a broader range and better signal quality. MVNOs, on the other hand, rely on the network coverage of the MNOs they partner with. An MVNO might have a limited range in specific areas compared to a traditional operator.
Are there any differences in service quality between MVNOs and traditional operators?
Service quality can vary between MVNOs and traditional operators. Traditional operators have more control over their network infrastructure and can prioritize customer resources. It can improve service quality, faster data speeds, and lower latency. However, many MVNOs offer comparable service quality as they leverage the network resources provided by the MNOs.
Can MVNOs offer the same features and services as traditional operators?
Yes, MVNOs can offer many features and services comparable to traditional operators. However, the offerings can vary depending on the agreements and partnerships between the MVNO and the MNO. Some MVNOs may have specific limitations or restrictions on accessing certain features or services.
Are there any cost differences between MVNOs and traditional operators?
MVNOs often differentiate themselves by offering competitive pricing and flexible plans compared to traditional operators. Since MVNOs do not have the exact infrastructure costs, they can pass on those savings to customers through more affordable programs or value-added services.
Can I keep my existing contact number when switching to an MVNO?
Yes, most MVNOs allow you to port your existing phone number when switching to their service. During signup, this process typically involves providing your current provider's account details to the MVNO.