Voice-over Internet Protocol (VoIP) codecs are more than just tools for audio compression and decompression. They are sophisticated algorithms that determine the quality, efficiency, and overall experience of your business VoIP communications. Understanding them requires a deeper look into their functionality, challenges, and the technology behind them.
What Are VoIP Codecs?
A codec, standing for “coder-decoder,” serves a dual function in VoIP systems: it compresses (encodes) and decompresses (decodes) digital audio data. This process is essential in converting analog voice signals into digital packets suitable for transmission over the internet and back into audible speech upon reception.
The primary objectives of a codec are
- Maintaining high audio quality
- Minimizing bandwidth consumption
- Reducing latency
Compression and Decompression
Compression reduces the size of audio files, which is essential for efficient network transmission. However, it’s a balancing act between file size and audio quality. Decompression, meanwhile, reconstructs the audio from the compressed data, aiming to reproduce the original sound as closely as possible.
VoIP Codec Types
Different VoIP codec types aim to meet different audio quality needs and network conditions. Let’s see how narrowband to ultra-wideband codecs shape your business communication experience.
- Narrowband Codecs: Designed for minimal bandwidth usage, narrowband codecs focus on a frequency range of 300Hz to 3.4kHz. They’re suitable for speech but may lack fidelity and richness.
- Wideband Codecs: These codecs cover a broader frequency range (50Hz to 7kHz or higher), providing clearer and more natural sound, improving intelligibility and listener comfort.
- Ultra-Wideband Codecs: Offering an even wider frequency range, ultra-wideband codecs deliver superior audio quality, replicating nuances in speech and tone.
Also Read: Top 10 VoIP Trends to Watch in 2024
Encoding, Decoding, and Containers
Encoding and decoding play a critical role in VoIP. Let’s understand them and how containers streamline these processes to deliver seamless audio communication across networks.
- Encoding Process: This involves converting analog voice signals into a digital format using the selected codec, optimizing the audio for transmission.
- Decoding Process: Upon reception, the digital audio is converted back into analog signals, aiming to reproduce the original audio accurately.
- Containers: In VoIP, containers package compressed audio data along with necessary metadata, facilitating the correct decoding and playback of the audio stream.
Discover the ideal VoIP codec for your business needs
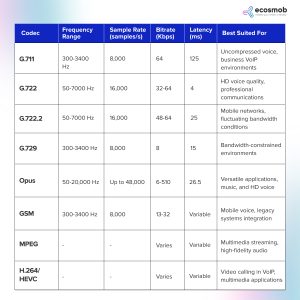
Key VoIP Codecs
If you’re a business using VoIP, you must familiarize yourself with the core VoIP codecs that are foundational to business communications. They are integral to balancing call quality, bandwidth requirements, and latency to meet diverse operational demands.
G.711 Codec
- Overview: G.711, prevalent in VoIP and traditional telephony, is known for its minimal compression, delivering high audio quality.
- Technicalities: It operates in two variants, A-law (used mainly in Europe) and µ-law (common in North America), with a bitrate of 64 kbps.
- Application: Ideal for high-bandwidth scenarios, it’s a go-to choice for businesses prioritizing call quality over bandwidth economy.
G.729 Codec
- Overview: G.729 is a highly efficient codec known for good audio quality at a significantly lower bitrate (about 8 kbps) than G.711.
- Compression Technique: It uses a form of lossy compression, employing a predictive algorithm that estimates and omits redundant data, making it suitable for low-bandwidth situations.
- Use Cases: Widely used when bandwidth is a premium, such as mobile VoIP applications and over-congested networks.
Other Notable VoIP Codecs
- G.722: A superior wideband codec offering better quality at a similar bitrate to G.711.
- G.722.2 (AMR-WB): Designed for wideband audio, this codec is optimized for wireless networks, providing high-quality voice transmission even in fluctuating network conditions.
- Opus: A highly flexible codec that dynamically adjusts its bitrate, bandwidth, and coding delay. It’s well-suited for various applications, from interactive voice to high-fidelity music streaming.
- H.264/H.265 (HEVC): Primarily video codecs, these are critical in VoIP for their efficiency in video conferencing. H.265 offers notable improvements in video quality and bandwidth usage over H.264.
- MPEG & VVC: These are advanced video codecs, with VVC being the latest standard offering improved compression efficiency. In VoIP, they are essential for multimedia transmission.
- GSM Codec: Initially developed for mobile voice, it has found a niche in VoIP due to its robustness in handling voice data efficiently over various network types.
VoIP Codec Challenges
From maintaining high audio quality to ensuring efficient bandwidth utilization, let’s see what challenges VoIP codecs face that affect real-time communication.
- Maintaining Quality: A VoIP codec’s key challenge is maintaining audio quality despite compression. This involves complex algorithms determining which audio parts can be compressed more heavily without impacting quality.
- Bandwidth Utilization: Codecs must optimize the audio data size to ensure efficient use of available bandwidth, which is especially important in constrained network environments.
- Latency and Jitter: Lower latency is crucial for real-time communication. Some codecs focus on faster processing and reduced data packets to minimize delay and jitter in voice transmission.
Choosing the Right VoIP Codec For Your Business
Making the right codec choice is critical for the success of your business communication. Learn how to navigate the trade-offs, and you’ll be able to select a VoIP codec that perfectly aligns with your company’s network capabilities and communication needs.
- Assessing Network Conditions: The codec choice is a trade-off between bandwidth efficiency and audio quality. Higher compression codecs save bandwidth but can introduce latency and degrade audio quality, which might be unacceptable in certain business settings. So, the selection often depends on the network’s bandwidth and reliability. For instance, a high-bandwidth network may favor a codec like G.711 for its superior audio quality, while a constrained network might require the efficiency of G.729.
- Compatibility with Hardware and Software: Not all codecs are supported by all devices and software. Selection involves ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure and considering the processing power required by more complex codecs.
Some codecs require more processing power and may not be compatible with older or less powerful hardware. Also, the VoIP software must support the chosen codec, and in cases of proprietary codecs, licensing might be a factor. - Latency Requirements: For real-time communications, such as in customer service scenarios, codecs with lower latency are preferred to ensure smooth and uninterrupted conversations.
- Codec Adaptability: Some modern codecs like Opus can adapt to changing network conditions by adjusting their bitrate and balancing quality and efficiency.
- Lossy Compression: Used by codecs like G.729, it significantly reduces file size by permanently removing certain audio information, affecting quality. While more efficient in terms of bandwidth, Lossy codecs sacrifice some audio quality.
- Lossless Compression: Though less common in VoIP, it retains the original audio quality perfectly but at the cost of larger file sizes and higher bandwidth requirements.
VoIP Codec Future Trends
As VoIP technology continues to evolve, we anticipate advancements in codec algorithms, focusing on AI and machine learning to further enhance audio quality and compression efficiency. Developing VoIP codecs that dynamically adapt to varying network conditions and user requirements will significantly improve the VoIP experience, making communications more seamless and effective.
Wrapping Up
VoIP codecs are the unsung heroes of your business communication, ensuring efficient, clear, and reliable communication. Understanding the nuances of different VoIP codecs will help you make informed decisions–whether you’re setting up a VoIP system, selecting a service, or developing VoIP solutions.
As the technology advances, we will see further advancements in codec efficiency, audio quality, and system compatibility, improving the VoIP experience.
Ready to elevate your business communications with the power of VoIP codecs? Let Ecosmob craft the perfect audio solution tailored to your needs. Contact us to ensure your voice is heard loud and clear!
Don't let poor-quality calls disrupt your business
FAQs
Why is codec selection important for my business?
Selecting the right codec ensures optimal call quality, efficient bandwidth usage, and reduced latency, enhancing your business communication.
Can the wrong codec affect my VoIP call quality?
Yes, choosing a codec that’s not suited to your network conditions can result in poor call quality and lag.
What is latency in VoIP communication?
Latency is the time delay in transmitting voice packets over the network, affecting real-time communication quality.
Are there VoIP codecs that adjust to network conditions?
Yes, codecs like Opus can dynamically adjust their bitrate based on network conditions to maintain call quality.
Are VoIP codecs secure from eavesdropping?
VoIP codecs do not provide encryption, but when paired with secure transport protocols like TLS and SRTP, they can help prevent eavesdropping.