QUICK SUMMARY
An Application-Level Gateway (ALG) enhances network security by inspecting and controlling application-specific traffic. This guide explores its functions, benefits, and deployment strategies, emphasizing its importance in modern cybersecurity.
In the ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, protecting network integrity has never been more crucial. Among the various security measures, an Application-Level Gateway (ALG), also known as an application-layer gateway, stands out due to its unique capabilities. Alongside ALGs, Session Border Controllers (SBCs) are pivotal in enhancing network security. The architecture of SBCs is designed to manage, secure, and regulate IP communications traffic. By integrating SBCs into the network, organizations can benefit from robust security features, such as intrusion prevention, fraud detection, and signaling and media encryption.
Understanding and deploying an ALG, complemented by the strategic use of SBC architecture, can significantly enhance your network security as cyber threats become more sophisticated. This guide will delve into what an ALG is, its functions, its role in modern security infrastructure, and why it’s indispensable in 2025.
What is an Application Level Gateway (ALG)?
An Application-Level Gateway (ALG) is a security component that operates at the OSI model’s application layer. Unlike traditional firewalls, which filter packets based solely on IP addresses and ports, ALGs provide deep inspection and filtering of application-specific data traffic. It allows them to manage, control, and secure applications more effectively.
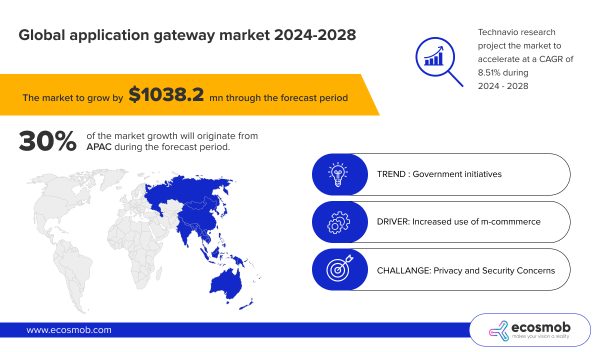
According to Technavio, the application gateway market is expected to grow significantly, with projections indicating an increase of USD 1038.2 million from 2024 to 2028, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.51% .
How Does an Application-Level Gateway Work?
An Application-Level Gateway operates by intercepting and analyzing application-specific traffic. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of its working mechanism:
Traffic Interception
When a user initiates a connection, the ALG acts as an intermediary and intercepts the traffic before it reaches the destination server. This interception allows the ALG to control and monitor the traffic flow immediately.
Packet Filtering
After intercepting the traffic, the ALG inspects each packet in detail. This process, called deep packet inspection, examines the application protocol and the packet content. By understanding the transmitted data, the ALG identifies potential threats and anomalies at a granular level.
Policy Enforcement
The ALG determines whether to allow or block traffic based on predefined security policies. These policies can be particular, targeting particular data types or application behavior. The ALG can also modify packets to comply with security requirements, such as sanitizing inputs to prevent SQL injection attacks.
Session Management
ALGs manage session states to ensure that connections are legitimate and secure. This involves tracking each session’s state, maintaining the communication’s integrity, and ensuring that only authorized sessions can continue. It is crucial for preventing session hijacking and other session-based attacks.
Protocol Translation
ALGs perform protocol translation in some scenarios to enable communication between different protocols. For example, an ALG might translate Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) messages to HTTP in VoIP applications, ensuring compatibility and seamless communication across various systems. This function is essential in environments where multiple protocols must interact securely and efficiently.
An Application-Level Gateway provides robust security by performing these functions, ensuring that only legitimate and secure application-specific traffic can pass through the network. This advanced level of inspection and control makes ALGs an essential component in modern network security infrastructures.
Functions of the Application Layer in ALGs
Understanding the application layer’s functions in the context of ALGs is crucial for grasping their importance. These functions enable ALGs to provide enhanced security and efficient traffic management, making them indispensable in modern network security strategies.
Application-Specific Filtering
ALGs filter traffic based on the application data, not just the headers. This capability allows them to block malicious content or commands within the application traffic. For instance, an ALG can block specific FTP commands or filter HTTP requests to prevent data leaks or attacks. By inspecting the actual content of the data packets, ALGs ensure that only legitimate and safe traffic is allowed through, significantly reducing the risk of security breaches.
Traffic Monitoring and Control
ALGs monitor real-time application traffic to provide detailed insights into network usage and potential threats. This monitoring helps administrators understand traffic patterns and identify unusual activities that could indicate security issues. ALGs dynamically adjust to control and manage traffic, ensuring the constant enforcement of security policies. This real-time adjustment capability helps maintain optimal performance and security, adapting to changing network conditions.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention
With their deep understanding of application protocols, ALGs can detect anomalies and potential intrusions at the application layer. This proactive approach helps prevent attacks before they cause significant damage. By analyzing application traffic behavior, ALGs can identify suspicious activities deviating from standard patterns, allowing quick intervention and mitigating threats. This defense layer is vital for protecting sensitive data and preserving the integrity of network operations.
These core functions emphasize the crucial role of the application layer in ALGs, demonstrating their capability to manage network traffic and enhance security effectively. By harnessing these capabilities, organizations can achieve robust protection while optimizing network performance.
Difference Between Traditional Firewalls and Application Level Gateway Firewalls
An Application Level Gateway Firewall combines the deep inspection capabilities of an ALG with the robust defense mechanisms of a firewall. This hybrid approach offers enhanced security by addressing threats at multiple layers.
Traditional Firewalls vs. Application-Level Gateway Firewalls
- Traditional Firewalls: These operate primarily at the network and transport layers, filtering packets based on IP addresses, ports, and essential packet attributes.
- Application Level Gateway Firewalls: These operate at the application layer, providing granular control and inspection of application-specific traffic. They can enforce rules based on the content of the traffic, not just its source or destination.
Key Benefits of Application-Level Gateway Firewalls
Application-level Gateway firewalls offer a range of benefits that make them a critical component of modern network security infrastructures. These benefits extend beyond traditional firewalls, offering enhanced security and more effective traffic management.
Enhanced Security
ALGs enhance security by inspecting data packets at the application layer to block malicious content like viruses and worms. They validate traffic protocols to prevent exploitation and detect anomalies to mitigate threats early, ensuring robust protection.
1. Deep Packet Inspection (DPI)
ALGs thoroughly inspect data packets at the application layer, ensuring that only legitimate and safe traffic is allowed. This detailed scrutiny helps to identify and block malicious content, such as viruses, worms, and application-layer attacks, providing a robust security defense.
2. Protocol Validation and Enforcement
By validating application-layer protocols, ALGs ensure traffic conforms to expected standards and behaviors. It prevents exploitation of protocol vulnerabilities and helps to enforce security policies consistently across the network.
3. Intrusion Detection and Prevention
ALGs can detect and prevent intrusions by analyzing traffic for anomalies and suspicious activities. This proactive approach helps identify and mitigate threats early before they cause significant damage.
Granular Traffic Control
ALGs provide granular traffic control by filtering data packets based on their content, allowing precise management of what is allowed or blocked. They dynamically adjust filtering rules based on traffic context, ensuring continuous enforcement of security policies.
1. Application-Specific Filtering
ALGs filter traffic based on the content of the data packets, allowing for more precise control over what is allowed or blocked. This capability is crucial for preventing data leaks and protecting sensitive information.
2. Dynamic Adjustment of Filtering Rules
Unlike traditional firewalls, ALGs can dynamically adjust their filtering rules based on the context and state of the traffic. This flexibility ensures that security policies are enforced continuously, adapting to changing network conditions and threats.
Improved Network Performance
By optimizing the handling of application-specific traffic, ALGs reduce latency and improve overall network performance. Efficient traffic management also leads to better resource utilization, resulting in lower operational costs and enhanced user experience.
1. Optimized Traffic Handling
ALGs can optimize the handling of application-specific traffic, reducing latency and improving the network’s overall performance. For example, by caching web pages or optimizing the flow of multimedia streams, ALGs enhance user experience.
2. Efficient Resource Utilization
By managing and controlling traffic more effectively, ALGs help to utilize network resources more efficiently. This results in better performance and lower operational costs, as the network can handle more traffic without compromising security.
Simplified Policy Management
ALGs offer centralized security management, making it easier to enforce consistent policies across the network. They also route traffic based on predefined security policies, ensuring data flows through the most secure and efficient paths.
1. Centralized Security Management
ALGs provide a centralized point for managing security policies, making it easier to enforce consistent policies across the entire network. It simplifies the administration and ensures that security measures are uniformly applied.
2. Policy-Based Traffic Routing
ALGs can route traffic based on predefined security policies, ensuring data flows through the most secure and efficient paths. This policy-based routing helps in maintaining the integrity and performance of the network.
Enhanced Visibility and Reporting
ALGs provide comprehensive reporting capabilities to track and analyze security incidents for quick and effective responses.
1. Detailed Traffic Insights
ALGs offer detailed insights into network traffic, giving administrators a clear view of usage patterns, potential threats, and overall network health. This visibility is crucial for effective network management and proactive threat mitigation.
2. Comprehensive Reporting
With comprehensive reporting capabilities, ALGs help organizations track and analyze security incidents, ensuring they respond quickly and effectively to potential threats.
ALGs enhance network security and performance by offering deep packet inspection, dynamic filtering, optimized traffic handling, and centralized policy management. Their ability to provide detailed insights and proactive threat prevention makes them essential to modern network security strategies.
What is ALG and What is Its Importance in Modern Networks?
ALGs are critical in modern network security because they provide deep visibility and control over application traffic. We must uphold the importance of Application Level Gateways in network security. It is essential as more businesses adopt cloud services, IoT devices, and other technologies that rely heavily on application-layer protocols. By providing deep packet inspection, protocol-specific filtering, and robust traffic control, ALGs enhance the overall security posture of networks. Whether referred to as an application-level gateway firewall, this technology is essential for defending against sophisticated cyber threats and ensuring the smooth operation of critical applications.
Deploying Application Level Gateways in 2025
As we move into 2025, the deployment of ALGs is becoming increasingly sophisticated. Here’s a detailed look at the steps and considerations for effectively deploying ALGs.
Assessing Network Needs
The first step in deploying an ALG is assessing your network’s needs. It involves understanding the types of applications in use, the nature of the traffic, and the potential threats.
Selecting the Right ALG Solution
With various ALG solutions available, selecting the right one is crucial. Consider factors such as the supported protocols, ease of management, scalability, and integration with existing security infrastructure.
Integration with Existing Security Measures
ALGs should complement your existing security measures, not replace them. Integrate ALGs with traditional firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and other security tools for a layered defense strategy.
Continuous Monitoring and Management
Deploying an ALG is not a set-and-forget solution. Continuous monitoring and management are essential to adapt to evolving threats and ensure optimal performance. Regular updates and configuration reviews are also necessary.
Application-level gateways require a strategic approach encompassing a thorough assessment of network needs, carefully selecting the right solution, seamless integration with existing security measures, and ongoing monitoring and management. By following these steps, organizations can enhance their security posture and ensure their networks are well-protected against emerging threats.
Effective Challenges and the Ways to Overcome ALG Deployment
Deploying an ALG comes with its own set of challenges. Here are some common obstacles and best practices to overcome them.
Protocol Complexity
One significant challenge in deploying an ALG is managing protocol complexity. Some protocols are highly complex and require deep packet inspection, making it difficult for the ALG to manage them efficiently. Regularly updating the ALG to handle new and complex protocols and ensuring the correct configuration to execute these protocols effectively is essential.
Performance Impact
Another challenge associated with ALGs is their potential to introduce latency and affect overall network performance due to the additional processing required. To mitigate this, optimizing ALG configurations and ensuring that the hardware or virtual machines running the ALGs have sufficient resources to handle the expected traffic loads is essential.
Compatibility Issues
Interactions between the ALG and specific applications or protocols can disrupt communication. Thorough testing before deployment is crucial to identifying and resolving compatibility issues, especially when dealing with complex environments like mobile app testing. Maintaining a list of supported applications and protocols can also help manage compatibility effectively.
Configuration Complexity
It presents another hurdle. Properly configuring an ALG can be complex and requires a deep understanding of the applications and network it supports. Comprehensive training for network administrators and detailed configuration guides can ensure the correct setup and management of the ALG.
Security Risks
It can arise from incorrectly configured ALGs, potentially allowing malicious traffic. Implementing strict security policies and conducting regular audits can ensure that the ALG is configured securely and operates as intended.
Scalability
It is a common challenge, especially in large or growing networks. Scaling ALGs to handle increasing network traffic can be difficult. Designing the network architecture with scalability in mind and using load balancing and clustering techniques to distribute traffic across multiple ALGs can address this issue effectively.
An application-level gateway involves several challenges, from managing protocol complexity to ensuring compatibility and scalability. However, organizations can overcome these challenges and enhance their network security and performance. By addressing these issues proactively, ALGs can be a powerful tool in safeguarding network communications and ensuring smooth operations.
Best Practices in ALG Deployment
ALGs are designed to manage the data packets transmitted across the network by specific applications. Let’s explore the best practices for deploying ALGs to ensure optimal security and performance.
1. Understanding the Role of ALGs
ALGs serve as intermediaries between the internal and external networks, managing and controlling the data traffic based on application-specific protocols. Their primary function is to inspect, modify, and control traffic at the application layer of the OSI model.
2. Selecting the Right ALG
When choosing an ALG, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the ALG supports your network’s specific applications and protocols.
- Scalability: Choose a solution that can scale with your network’s growth.
- Security Features: Look for advanced security features like deep packet inspection and intrusion detection.
3. Deployment Planning
Proper planning is crucial for successful ALG deployment. Follow these steps:
- Network Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of your network architecture and traffic patterns.
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline the goals you aim to achieve with ALG deployments, such as enhanced security, improved performance, or compliance with regulations.
- Resource Allocation: Ensure adequate resources (hardware and software) are allocated for the deployment process.
4. Configuration Best Practices
Effective configuration of your ALG can significantly impact its performance and security:
- Protocol-Specific Configuration: You can customize the ALG settings for different application protocols (e.g., SIP, FTP, HTTP).
- Rule Management: Define rules to control traffic flow, ensuring only legitimate traffic is allowed.
- Logging and Monitoring: Enable comprehensive logging and real-time monitoring to promptly detect and respond to suspicious activities.
5. Security considerations
To maximize the security benefits of ALGs, implement the following practices:
- Regular Updates: Keep your ALG software updated with the latest patches and security updates.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to limit who can modify ALG configurations.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Integrate threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
6. Performance Optimization
Optimizing the performance of your ALG involves balancing security and efficiency:
- Load Balancing: Use load balancing techniques to distribute traffic evenly across multiple ALGs, preventing bottlenecks.
- Resource Management: Monitor resource usage and adjust configurations to avoid performance degradation.
- Traffic Prioritization: Prioritize critical application traffic to ensure high availability and responsiveness.
7. Testing and Validation
Before going live, thoroughly test your ALG deployment:
- Functional Testing: Verify that the ALG correctly handles and secures traffic for all supported applications.
- Performance Testing: Assess the impact of the ALG on network performance under various load conditions.
- Security Testing: Conduct penetration testing to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
8. Continuous Improvement
ALG deployment is not a one-time task but an ongoing process:
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure compliance with security policies and identify areas for improvement.
- User Feedback: Collect and analyze feedback from users to address any issues and enhance the ALG’s overall performance.
- Training and Awareness: Provide continuous training to network administrators on the latest ALG features and best practices.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your ALG deployment is both effective and efficient, providing robust security and optimal performance. Stay proactive with regular updates, monitoring, and continuous improvement to maintain a secure and resilient network environment.
The Future of Application-Level Gateways
As we look to the future, we expect ALGs to evolve and adapt to new cybersecurity challenges. Here are some trends to watch out for in 2025 and beyond.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Integrating AI and machine learning into ALGs will significantly detect and respond to threats. These technologies can analyze traffic patterns, detect anomalies, and quickly adapt security measures.
Cloud-Based ALGs
With the increasing adoption of cloud services, cloud-based ALGs are becoming more prevalent. These solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and ease of management, making them ideal for modern, dynamic networks.
Increased Focus on Privacy
As data privacy becomes a significant concern, ALGs will protect sensitive information during transmission. Enhanced encryption and data masking techniques will be integral to ALG solutions.
By embracing these trends, organizations can ensure that their network security remains robust and adaptive in the face of evolving threats. The future of ALGs looks promising, with advancements that will continue to safeguard and optimize network communications.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, an Application Level Gateway is critical to modern network security. Its ability to inspect and control application-specific traffic provides a robust defense against cyber threats. As we move into 2025, understanding and deploying ALGs will be essential for any organization looking to maintain a secure network environment. By staying updated with the best practices and latest trends, Ecosmob Technologies can leverage the full potential of ALGs to enhance your cybersecurity posture. Our experts are always available 24/7 for your assistance.
FAQs
What is an Application Level Gateway?
An application-level gateway (ALG) is a security component that inspects and filters application-specific traffic to protect networks from application-layer attacks. It ensures that the data exchanged through specific applications is secure and complies with security policies.
How does an ALG differ from a traditional firewall?
Unlike traditional firewalls that operate at the network or transport layer, ALGs function at the application layer, providing more granular traffic inspection and control. It allows ALGs to understand and filter the content of application data, offering enhanced security.
Why is an ALG necessary for VoIP security?
ALGs validate and secure SIP traffic, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of VoIP communications. They prevent issues such as eavesdropping and spoofing, common threats in VoIP environments.
How do ALGs enhance threat detection?
By inspecting application-specific traffic, ALGs can identify and mitigate advanced threats that traditional firewalls might miss. Their ability to analyze the content and context of data exchanges makes them effective against complex attacks.
What is the role of an ALG in web application security?
ALGs protect web applications by scrutinizing HTTP traffic, preventing threats like data breaches and unauthorized access. They ensure that web traffic adheres to security policies, reducing the risk of exploitation.








![SIP Protocol [SIP Signalling]](https://a4f8b050.delivery.rocketcdn.me/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/Blog-79.jpg)